Technology in advanced manufacturing systems is transforming production landscapes. The integration of artificial intelligence enhances decision-making while robotics and automation streamline operations. Additionally, the Internet of Things facilitates real-time data flow, improving efficiency. However, these advancements come with challenges such as workforce adaptation and integration hurdles. Understanding how these technologies interact and their implications for sustainability could reshape the future of manufacturing as industries seek greater competitiveness. What strategies will emerge to address these challenges?
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing
As manufacturing processes continue to evolve, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a pivotal force driving efficiency and innovation.
Machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets to optimize production schedules and enhance quality control.
Additionally, predictive maintenance utilizes AI to anticipate equipment failures, minimizing downtime and reducing costs.
This integration of AI empowers manufacturers to achieve greater operational freedom and adaptability in an increasingly competitive landscape.
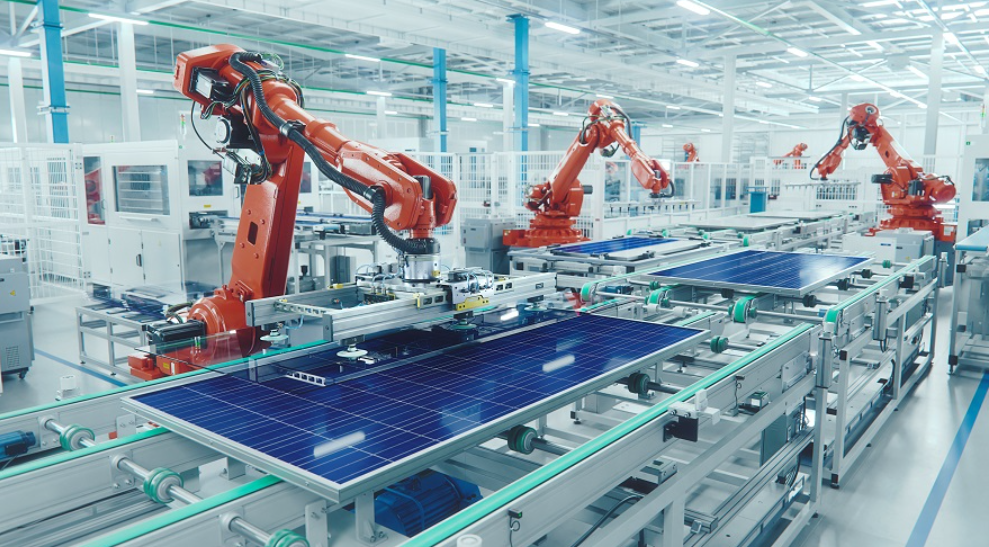
Advancements in Robotics and Automation
Although many industries have long relied on manual labor, recent advancements in robotics and automation are transforming manufacturing environments into highly efficient and flexible operations.
Robotic collaboration facilitates seamless interaction between machines and humans, enhancing productivity.
However, automation challenges persist, including integration complexities and workforce adaptation.
Addressing these issues is essential for fully harnessing the potential of advanced robotic technologies in manufacturing processes.
The Impact of the Internet of Things on Production Efficiency
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) into manufacturing processes significantly enhances production efficiency by enabling real-time monitoring and data analysis.
Smart factories leverage interconnected devices to collect and analyze data, optimizing workflows and reducing downtime.
This data-driven approach fosters informed decision-making, allowing manufacturers to respond swiftly to changes, ultimately improving overall productivity and operational agility in a competitive market.
Sustainable Practices in Advanced Manufacturing Systems
While the pursuit of efficiency and productivity has traditionally dominated manufacturing priorities, an increasing emphasis on sustainable practices is reshaping advanced manufacturing systems.
Incorporating renewable energy sources significantly reduces carbon footprints, while innovative waste reduction strategies streamline operations.
These changes not only enhance environmental stewardship but also promote long-term economic viability, aligning manufacturing processes with a growing demand for sustainability in the global market.
Conclusion
In a world where machines increasingly dictate the tempo of production, one might ironically ponder if humanity is truly in control. As advanced manufacturing systems harness artificial intelligence, robotics, and the Internet of Things, efficiency surges while the workforce grapples with adaptation. However, the promise of sustainable practices and cost reduction raises an eyebrow—could the very technologies designed to liberate us instead entrap us in a cycle of complexity? Ultimately, the balance between innovation and human oversight remains a delicate dance.